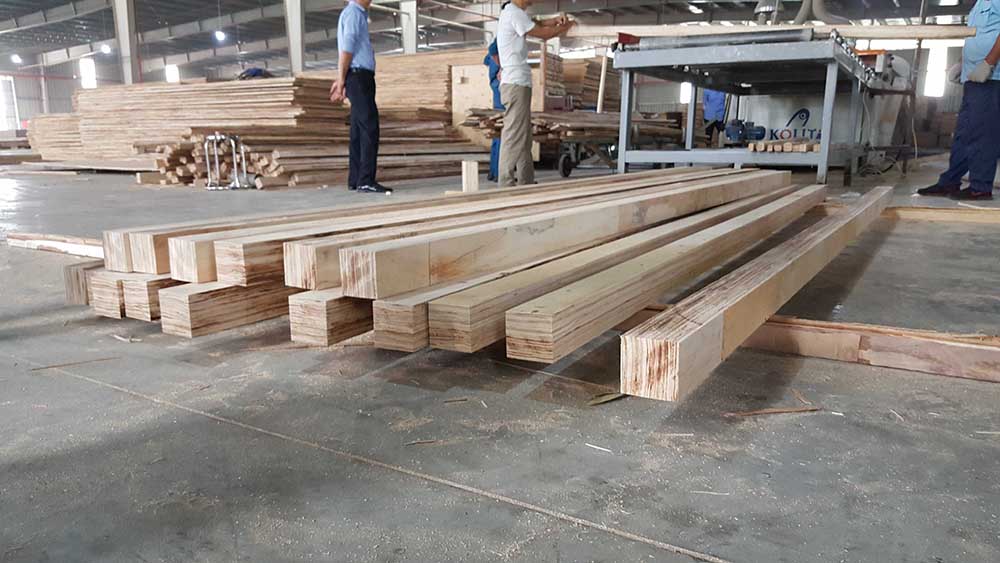
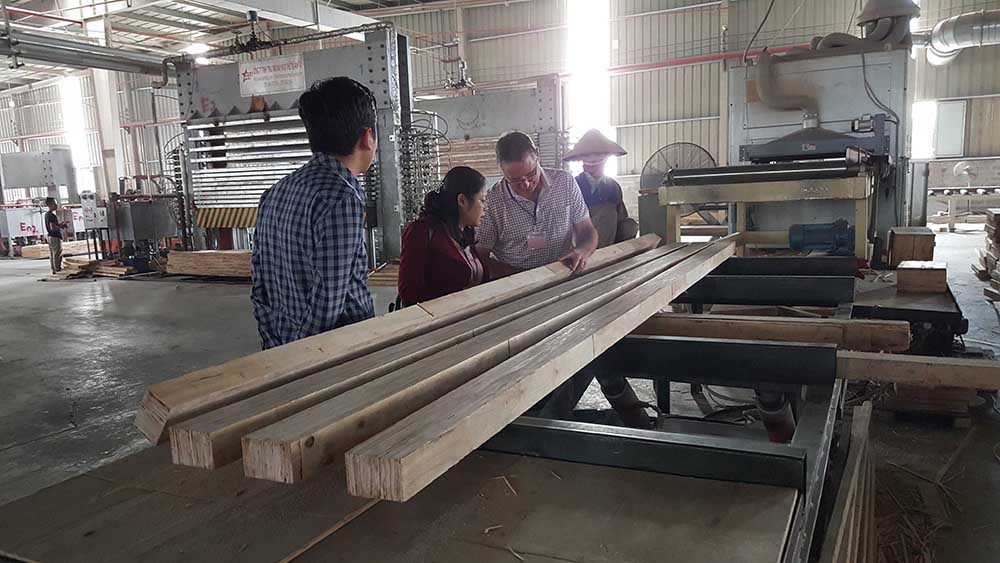
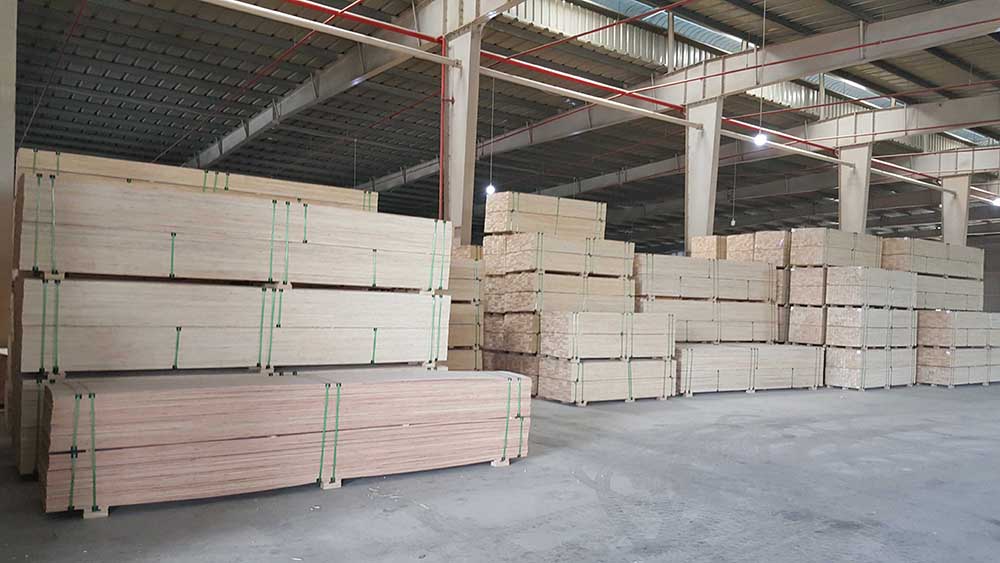
LVL
Laminated veneer lumber (LVL) is an engineered wood product that uses multiple layers of thin wood assembled with adhesives. It is typically used for headers, beams, rimboard, and edge-forming material
Table of contents
1. LVL Specification
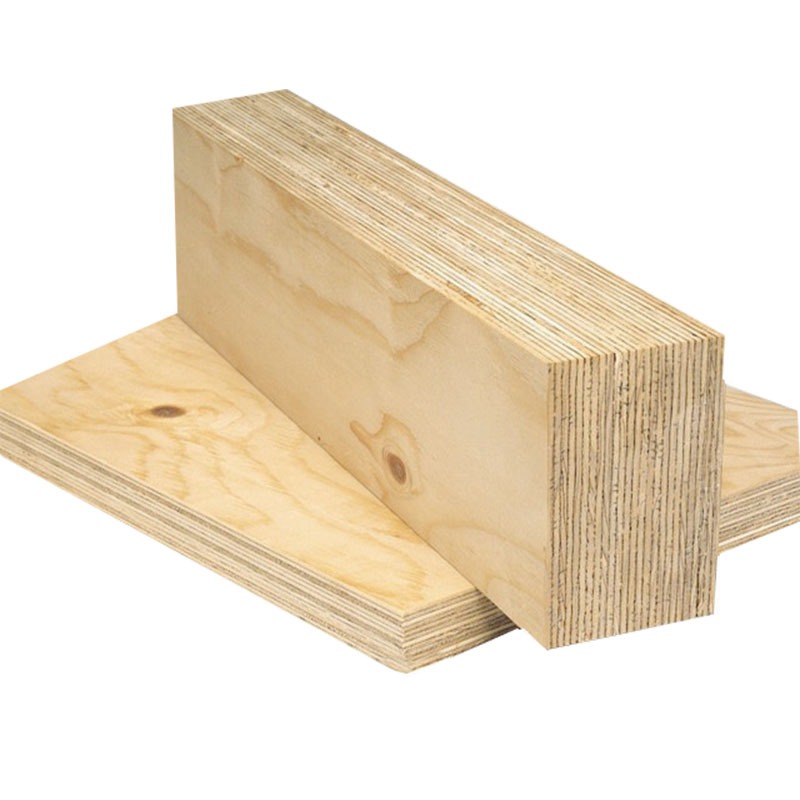

| Size | Length up to 4000mm Thickness up to 50mm |
| Face & back | A grade veneer |
| Core | Mixed hardwood / Mixed lightwood |
| Glue type | E1 & E2 Formaldehylde Emission Standard |
| Tolerance | +/- 0.5mm |
| Moisture level | Below 15% |
| Grade | Sanding grade for furniture parts No sanding grade for packing |
2. How to produce LVL by Kim Global
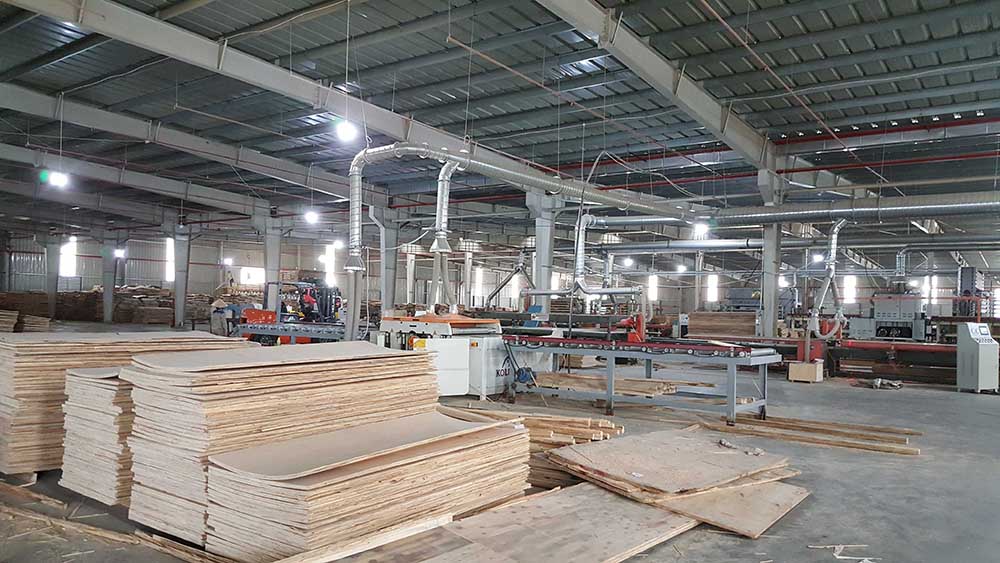
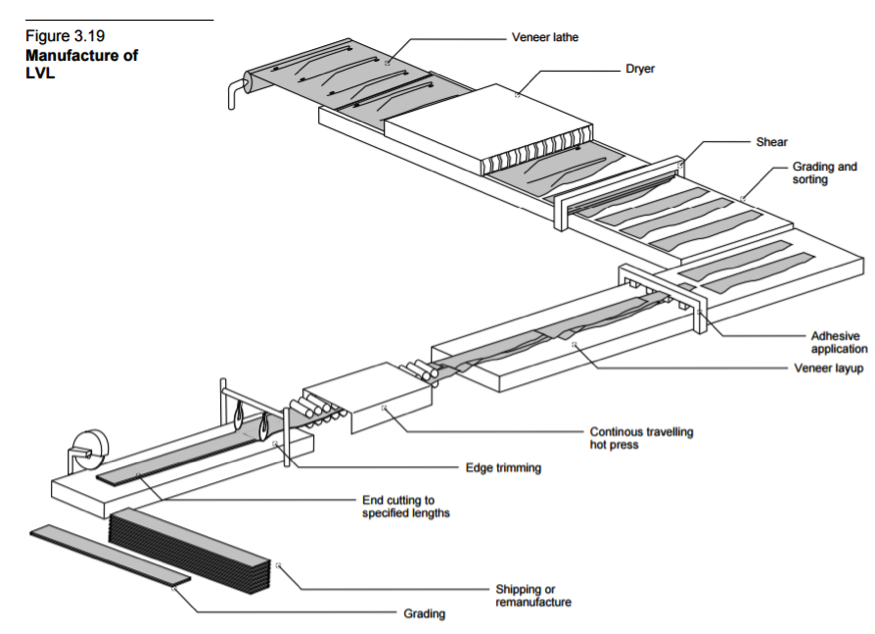
The process of manufacturing laminated veneer lumber (LVL) generally follows the manufacturing steps as depicted in Figure 1. The log is debarked and is then conditioned in a hot bath for an efficient veneer production. Veneer sheets, varying in thickness from 2.5mm to 4.8mm, are formed by rotating a log on a veneer lathe, and typically measure 2.4 to 18.8 m long by 0.6 to 1.2 m wide. A dryer is then used to reach a target moisture content varying between 6 and 10%. Defects that have an impact on the strength of the dried veneer sheets are trimmed away before grading the sheets, which can be done using ultrasonic testing. After an adhesive is applied to the top face of the sheets, usually phenol-formaldehyde, they are piled up so that end joints of each sheet are staggered along the billet. Consequently, the end joints’ influence on strength is greatly reduced. Those end joints can be either butt, scarf or finger joints. As an alternative, the individual veneer sheets may be overlapped to allow a proper load transfer. The mat then goes through a continuous press that applies pressure and heat to compact it and cure the resin. Finally, the billets are ripped and sawn to the required widths and lengths, which typically correspond to framing pieces such as beams. However, certain manufacturers produce formats of LVL that correspond to panels rather than framing members. The species for LVL production commonly include Douglas Fir, Larch, Southern Yellow Pine, and Poplar, while Lodgepole Pine, Western Hemlock, Red Maple, and Southern Pine may also be used though less frequently.
Cross-banded LVL, a variation of LVL, respects the same manufacturing steps described above, with one or two of the veneers having the grain running perpendicular to their longitudinal axis as opposed to running parallel to it.
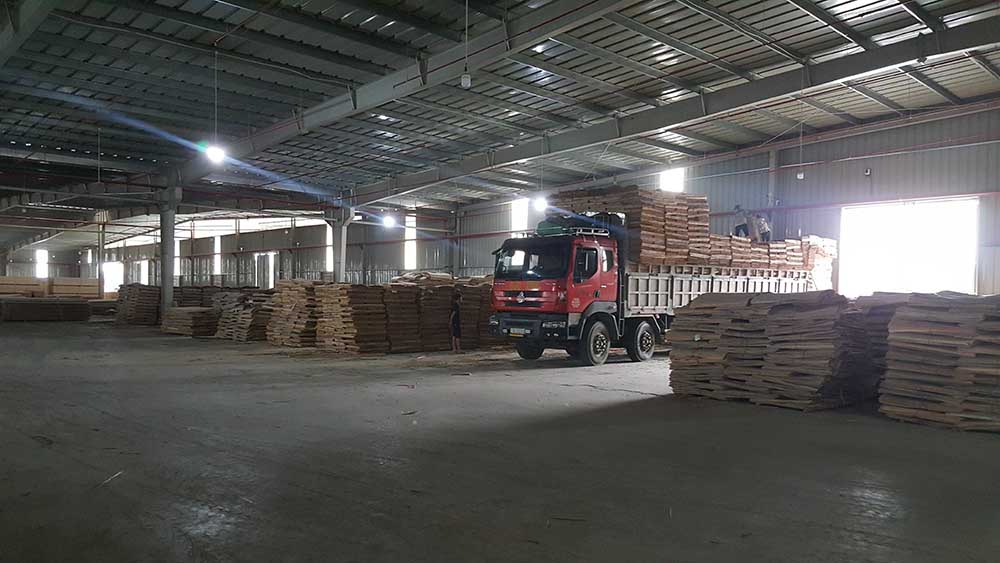
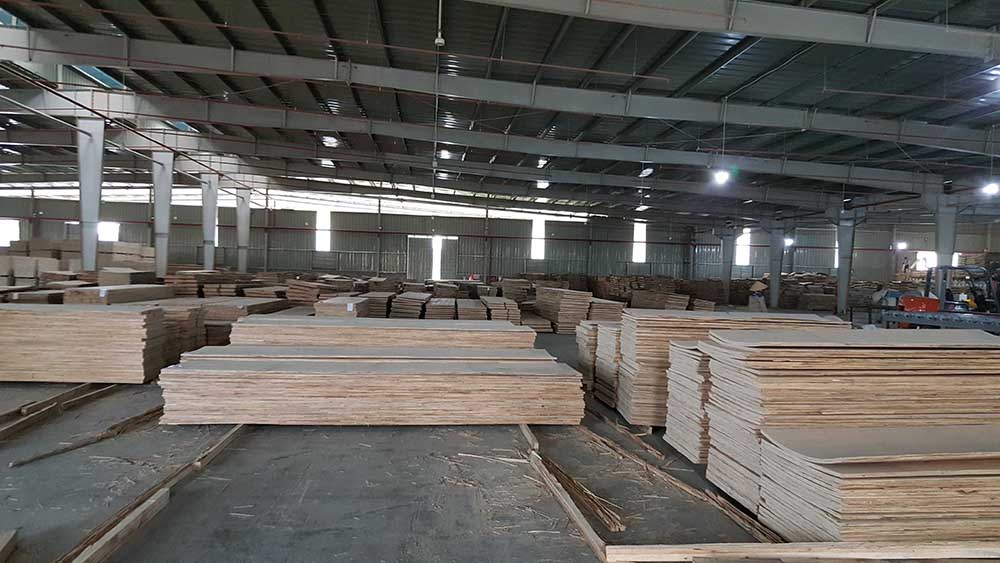
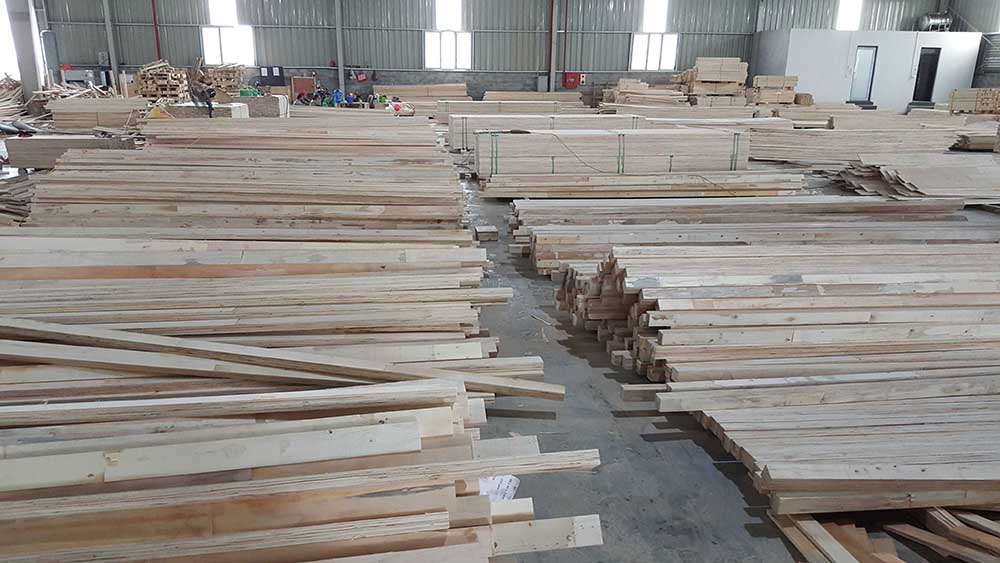
3. LVL images









